LoRa-Bee
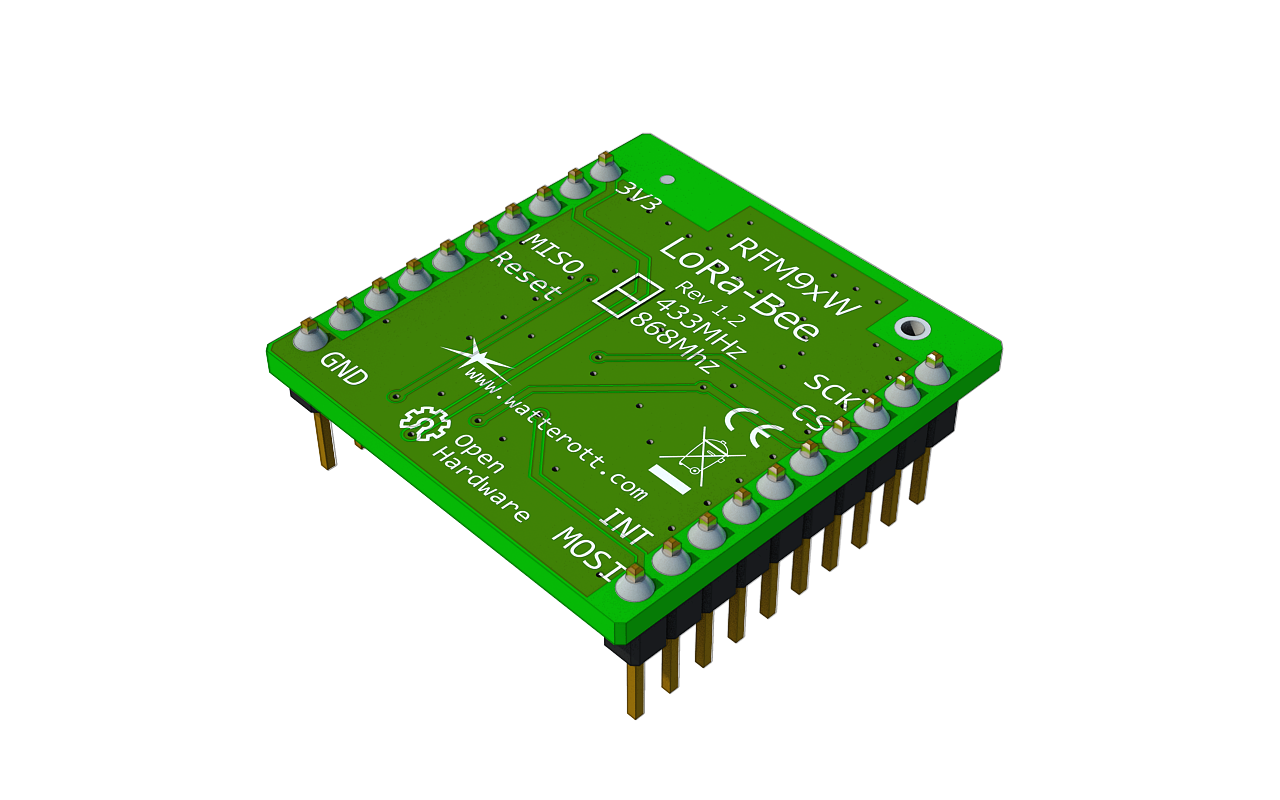
Technische Informationen
- HopeRF RFM95W/RFM96W LoRa Transceiver
- LoRa-Bee 868 / 915 MHz nutzt RFM95W (SX1276 kompatibel)
- LoRa-Bee 433 / 470 MHz nutzt RFM96W (SX1276 kompatibel)
- SPI interface
- Bezeichnung: RFN9xW
- Maße: 46mm x 25mm x 12mm
- Gewicht: 1,1 g
Hinweise
Bitte prüfe bevor du dir eine senseBox mit LoRa Bee holst, ob dein Gebiet bereits von LoRa erschlossen ist: https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/community#list-communities-map
Achtung: Aufgrund der erhöhten Komplexität der Installation empfehlen wir das LoRa-Modul außschließlich fortgeschrittenen Nutzern von Open-Hardware
Upload über LoRaWAN
Es ist möglich Sensordaten per LoRaWAN™ durch das TheThingsNetwork (TTN) auf die openSenseMap zu laden. LoRa ist ein zunehmend Verbreitung findender Funkstandard, welcher ähnlich wie WiFi digitale Datenübertragung in einem IP-Netzwerk erlaubt, jedoch deutlich andere Features bietet:
- Datendurchsatz: 300 - 3000 Bit/s
- Reichweite: bis zu 15km
TTN ist eins von mehreren Projekten, welches die zur Funk-Hardware zugehörige Infrastruktur für das IP-Netzwerk implementiert, wodurch registrierte Geräte mit dem Internet verbunden werden können.
Nutzer können Gateways sowie Nodes zu dem Netzwerk hinzufügen.
TTN openSenseMap Integration
Die openSenseMap bietet eine direkte Integration in das TTN Netzwerk, was die Konfiguration stark vereinfacht. Hierfür musst du einen Account TheThingsNetwork erstellen.
Registrierung in TTN Console
Um ein Gerät in das TTN einzubinden, muss für dieses zunächst unter
thethingsnetwork.org
eine Application und ein Device registriert werden. Hierbei erhält man eine
app_id und eine dev_id.
Für die registrierte Application muss die HTTP Integration unter https://console.thethingsnetwork.org/applications/DEINE_APPID/integrations/create/http-ttn
aktiviert werden. Diese muss konfiguriert werden, dass sie die Nachrichten von
Devices per POST an https://ttn.opensensemap.org/v1.1 weiterleitet. Das
Authorization-Feld kann leer bleiben!
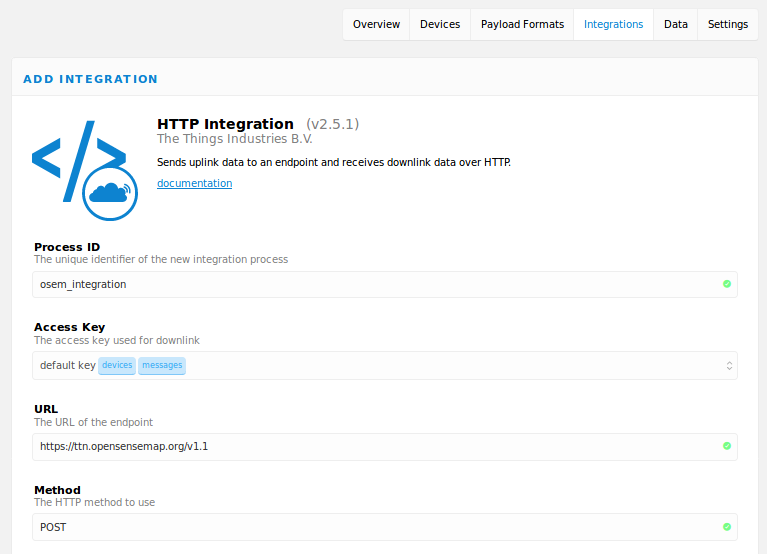
Für die Datenübertragung zur openSenseMap müssen die app_id und dev_id bei
der Registrierung auf der openSenseMap in der TTN-Konfiguration angegeben
werden. Darüber hinaus muss ein passendes Decoding-Profil konfiguriert werden,
welches bestimmt wie die - wegen der geringen Bandbreite als rohe Bytes
übertragenen - Daten als Messungen interpretiert werden sollen.
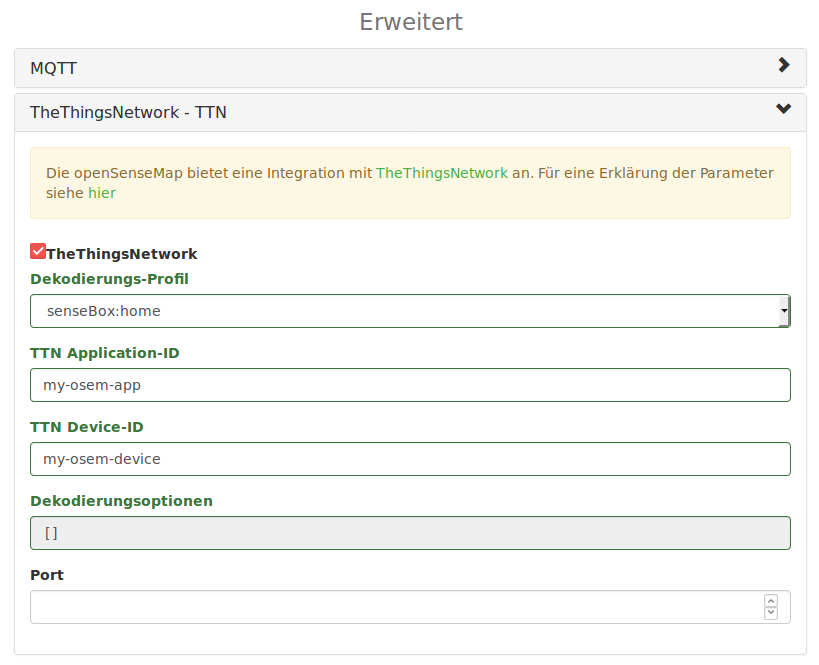
Optional kann im Feld port noch der Port angegeben werden, auf welchem
der Sender seine Daten an das TTN schickt. So lassen sich die selbe app_id
und dev_id für mehrere Sensorstationen verwenden.
Arduino Sketch
So könnte ein Arduino Sketch aussehen, mit dem du Daten über das TTN-Netzwerk an die openSenseMap senden kannst. Mit diesem Sketch werden die Phänomene:Lufttemperatur, Luftfeuchte, PM10, PM2.5, UV-Intensität, Beleuchtungsstärke und Luftdruck gemessen.
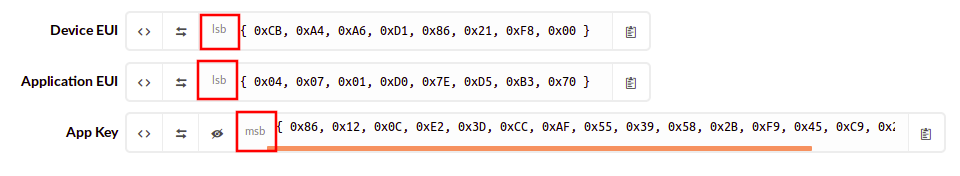
Achte darauf, dass auf der TTN-Homepage du für die Device-EUI und die Application-EUI das lsb-Format und für den App-Key das msb-Format ausgewählt hast!
Deklarieren der globalen Variablen und Deffinierung der Sensoren
/*
senseBox:home - Citizen Sensingplatform
Version: lorav2.0.0
Date: 2018-09-11
Homepage: https://www.sensebox.de https://www.opensensemap.org
Author: Reedu GmbH & Co. KG
Note: Sketch for senseBox:home LoRa MCU Edition
Model: homeV2lora
Email: support@sensebox.de
Code is in the public domain.
https://github.com/sensebox/node-sketch-templater
*/
#include <LoraMessage.h>
#include <lmic.h>
#include <hal/hal.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <senseBoxIO.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_HDC1000.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP280.h>
#include <Makerblog_TSL45315.h>
#include <VEML6070.h>
#include <SDS011-select-serial.h>
// Uncomment the next line to get debugging messages printed on the Serial port
// Do not leave this enabled for long time use
#define ENABLE_DEBUG
#ifdef ENABLE_DEBUG
#define DEBUG(str) Serial.println(str)
#else
#define DEBUG(str)
#endif
// Connected sensors
// Temperatur
#define HDC1080_CONNECTED
// rel. Luftfeuchte
#define HDC1080_CONNECTED
// Luftdruck
#define BMP280_CONNECTED
// Beleuchtungsstärke
#define TSL45315_CONNECTED
// UV-Intensität
#define VEML6070_CONNECTED
// PM10
#define SDS011_CONNECTED
// Number of serial port the SDS011 is connected to. Either Serial1 or Serial2
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
#define SDS_UART_PORT (Serial1)
#endif
//Load sensors / instances
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
Adafruit_HDC1000 HDC = Adafruit_HDC1000();
float temperature = 0;
float humidity = 0;
#endif
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
Adafruit_BMP280 BMP;
double pressure;
#endif
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
uint32_t lux;
Makerblog_TSL45315 TSL = Makerblog_TSL45315(TSL45315_TIME_M4);
#endif
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
VEML6070 VEML;
uint16_t uv;
#endif
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
SDS011 SDS(SDS_UART_PORT);
float pm10 = 0;
float pm25 = 0;
#endif
Nun müssen wir im Sketch die eben erstellten Device und Application EUI's sowie den App Key eingeben
Einfügen der Device und Application EUI und App Key
// This EUI must be in little-endian format, so least-significant-byte
// first. When copying an EUI from ttnctl output, this means to reverse
// the bytes. For TTN issued EUIs the last bytes should be 0xD5, 0xB3,
// 0x70.
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPEUI[8]= {DIE APPLICATION EUI HIER(lsb-Format)};
void os_getArtEui (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, APPEUI, 8);}
// This should also be in little endian format, see above.
static const u1_t PROGMEM DEVEUI[8]={DIE DEVICE EUI HIER(lsb-Format)};
void os_getDevEui (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, DEVEUI, 8);}
// This key should be in big endian format (or, since it is not really a
// number but a block of memory, endianness does not really apply). In
// practice, a key taken from ttnctl can be copied as-is.
// The key shown here is the semtech default key.
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPKEY[16] ={DER APP KEY HIER(msb-Format)};
void os_getDevKey (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, APPKEY, 16);}
Nachfolgend geben wir ein Interval an in welchen die Daten an das TTN-Netzwerk geschickt werden sollen. In diesem Sketch beträgt das Intervall alle 60 Sekunden. Des weiteren werden die Pins gemappt und eine onEvent()-Funktion zum Debuggen im Seriellen Monitor wird erstellt.
Intervall, Mapping und Debug
static osjob_t sendjob;
// Schedule TX every this DemaJetny seconds (might become longer due to duty
// cycle limitations).
const unsigned TX_INTERVAL = 60;
// Pin mapping
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = PIN_XB1_CS,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.dio = {PIN_XB1_INT, PIN_XB1_INT, LMIC_UNUSED_PIN},
};
void onEvent (ev_t ev) {
senseBoxIO.statusGreen();
DEBUG(os_getTime());
switch(ev) {
case EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT:
DEBUG(F("EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_FOUND:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_FOUND"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_MISSED:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_MISSED"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_TRACKED:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_TRACKED"));
break;
case EV_JOINING:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOINING"));
break;
case EV_JOINED:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOINED"));
// Disable link check validation (automatically enabled
// during join, but not supported by TTN at this time).
LMIC_setLinkCheckMode(0);
break;
case EV_RFU1:
DEBUG(F("EV_RFU1"));
break;
case EV_JOIN_FAILED:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_REJOIN_FAILED:
DEBUG(F("EV_REJOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_TXCOMPLETE:
DEBUG(F("EV_TXCOMPLETE (includes waiting for RX windows)"));
if (LMIC.txrxFlags & TXRX_ACK)
DEBUG(F("Received ack"));
if (LMIC.dataLen) {
DEBUG(F("Received "));
DEBUG(LMIC.dataLen);
DEBUG(F(" bytes of payload"));
}
// Schedule next transmission
os_setTimedCallback(&sendjob, os_getTime()+sec2osticks(TX_INTERVAL), do_send);
break;
case EV_LOST_TSYNC:
DEBUG(F("EV_LOST_TSYNC"));
break;
case EV_RESET:
DEBUG(F("EV_RESET"));
break;
case EV_RXCOMPLETE:
// data received in ping slot
DEBUG(F("EV_RXCOMPLETE"));
break;
case EV_LINK_DEAD:
DEBUG(F("EV_LINK_DEAD"));
break;
case EV_LINK_ALIVE:
DEBUG(F("EV_LINK_ALIVE"));
break;
default:
DEBUG(F("Unknown event"));
break;
}
}
LoRaMessage message deklarieren wir das Paket message welchen sukzessiv die Messwerte unserer Sensoren hinzugefügt wird.
Erstellen der LoRa-Message
void do_send(osjob_t* j){
// Check if there is not a current TX/RX job running
if (LMIC.opmode & OP_TXRXPEND) {
DEBUG(F("OP_TXRXPEND, not sending"));
} else {
LoraMessage message;
//-----Temperature-----//
//-----Humidity-----//
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("Temperature: "));
temperature = HDC.readTemperature();
DEBUG(temperature);
message.addUint16((temperature + 18) * 771);
delay(2000);
DEBUG(F("Humidity: "));
humidity = HDC.readHumidity();
DEBUG(humidity);
message.addHumidity(humidity);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----Pressure-----//
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
float altitude;
pressure = BMP.readPressure()/100;
altitude = BMP.readAltitude(1013.25); //1013.25 = sea level pressure
DEBUG(F("Pressure: "));
DEBUG(pressure);
message.addUint16((pressure - 300) * 81.9187);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----Lux-----//
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("Illuminance: "));
lux = TSL.readLux();
DEBUG(lux);
message.addUint8(lux % 255);
message.addUint16(lux / 255);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----UV intensity-----//
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("UV: "));
uv = VEML.getUV();
DEBUG(uv);
message.addUint8(uv % 255);
message.addUint16(uv / 255);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----PM-----//
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
uint8_t attempt = 0;
while (attempt < 5) {
bool error = SDS.read(&pm25, &pm10);
if (!error) {
DEBUG(F("PM10: "));
DEBUG(pm10);
message.addUint16(pm10 * 10);
DEBUG(F("PM2.5: "));
DEBUG(pm25);
message.addUint16(pm25 * 10);
break;
}
attempt++;
}
#endif
// Prepare upstream data transmission at the next possible time.
LMIC_setTxData2(1, message.getBytes(), message.getLength(), 0);
DEBUG(F("Packet queued"));
}
// Next TX is scheduled after TX_COMPLETE event.
}
Anschließend folgt die setup()-Funktion die du es aus den bisherigen Arduino-Sketches bereits kennen solltest. In dieser starten wir unsere Sensoren und den seriellen Monitor.
setup()-Funktion
void setup() {
#ifdef ENABLE_DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600);
#endif
delay(3000);
// RFM9X (LoRa-Bee) in XBEE1 Socket
senseBoxIO.powerXB1(false); // power off to reset RFM9X
delay(250);
senseBoxIO.powerXB1(true); // power on
// Sensor initialization
DEBUG(F("Initializing sensors..."));
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
VEML.begin();
delay(500);
#endif
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
HDC.begin();
#endif
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
BMP.begin(0x76);
#endif
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
TSL.begin();
#endif
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
SDS_UART_PORT.begin(9600);
#endif
DEBUG(F("Sensor initializing done!"));
DEBUG(F("Starting loop in 3 seconds."));
delay(3000);
// LMIC init
os_init();
// Reset the MAC state. Session and pending data transfers will be discarded.
LMIC_reset();
// Start job (sending automatically starts OTAA too)
do_send(&sendjob);
}
Zu guter letzt fehlt jetzt noch die loop()-Funktion. In dieser wird deklariert, dass der in den globalen Variablen deffinierte os_loop() ausgeführt wird.
loop()-Funktion
void loop() {
os_runloop_once();
}
Zum einfachen Copy&Paste hier der gesamte Sketch. Denk daran deine eigenen ID's und den App Key einzugeben.
Gesamter Sketch
/*
senseBox:home - Citizen Sensingplatform
Version: lorav2.0.0
Date: 2018-09-11
Homepage: https://www.sensebox.de https://www.opensensemap.org
Author: Reedu GmbH & Co. KG
Note: Sketch for senseBox:home LoRa MCU Edition
Model: homeV2lora
Email: support@sensebox.de
Code is in the public domain.
https://github.com/sensebox/node-sketch-templater
*/
#include <LoraMessage.h>
#include <lmic.h>
#include <hal/hal.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <senseBoxIO.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_HDC1000.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP280.h>
#include <Makerblog_TSL45315.h>
#include <VEML6070.h>
#include <SDS011-select-serial.h>
// Uncomment the next line to get debugging messages printed on the Serial port
// Do not leave this enabled for long time use
#define ENABLE_DEBUG
#ifdef ENABLE_DEBUG
#define DEBUG(str) Serial.println(str)
#else
#define DEBUG(str)
#endif
// Connected sensors
// Temperatur
#define HDC1080_CONNECTED
// rel. Luftfeuchte
#define HDC1080_CONNECTED
// Luftdruck
#define BMP280_CONNECTED
// Beleuchtungsstärke
#define TSL45315_CONNECTED
// UV-Intensität
#define VEML6070_CONNECTED
// PM10
#define SDS011_CONNECTED
// Number of serial port the SDS011 is connected to. Either Serial1 or Serial2
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
#define SDS_UART_PORT (Serial1)
#endif
//Load sensors / instances
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
Adafruit_HDC1000 HDC = Adafruit_HDC1000();
float temperature = 0;
float humidity = 0;
#endif
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
Adafruit_BMP280 BMP;
double pressure;
#endif
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
uint32_t lux;
Makerblog_TSL45315 TSL = Makerblog_TSL45315(TSL45315_TIME_M4);
#endif
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
VEML6070 VEML;
uint16_t uv;
#endif
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
SDS011 SDS(SDS_UART_PORT);
float pm10 = 0;
float pm25 = 0;
#endif
//measurement variables
const int GAUGE_PIN = 6; // Pin connected to reed switch
unsigned int rainCounter = 0;
// This EUI must be in little-endian format, so least-significant-byte
// first. When copying an EUI from ttnctl output, this means to reverse
// the bytes. For TTN issued EUIs the last bytes should be 0xD5, 0xB3,
// 0x70.
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPEUI[8]={ 0x33, 0x2F, 0x01, 0xD0, 0x7E, 0xD5, 0xB3, 0x70 };
void os_getArtEui (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, APPEUI, 8);}
// This should also be in little endian format, see above.
static const u1_t PROGMEM DEVEUI[8]={ 0x48, 0x33, 0xD0, 0x7A, 0xE7, 0xA7, 0x5D, 0x00 };
void os_getDevEui (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, DEVEUI, 8);}
// This key should be in big endian format (or, since it is not really a
// number but a block of memory, endianness does not really apply). In
// practice, a key taken from ttnctl can be copied as-is.
// The key shown here is the semtech default key.
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPKEY[16] ={ 0xAC, 0x9E, 0x89, 0x27, 0x70, 0x06, 0xAF, 0x89, 0xC3, 0xB3, 0xE0, 0xA6, 0x3F, 0x74, 0x1C, 0x23 };
void os_getDevKey (u1_t* buf) { memcpy_P(buf, APPKEY, 16);}
static osjob_t sendjob;
// Schedule TX every this DemaJetny seconds (might become longer due to duty
// cycle limitations).
const unsigned TX_INTERVAL = 60;
// Pin mapping
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = PIN_XB1_CS,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.dio = {PIN_XB1_INT, PIN_XB1_INT, LMIC_UNUSED_PIN},
};
void onEvent (ev_t ev) {
senseBoxIO.statusGreen();
DEBUG(os_getTime());
switch(ev) {
case EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT:
DEBUG(F("EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_FOUND:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_FOUND"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_MISSED:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_MISSED"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_TRACKED:
DEBUG(F("EV_BEACON_TRACKED"));
break;
case EV_JOINING:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOINING"));
break;
case EV_JOINED:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOINED"));
// Disable link check validation (automatically enabled
// during join, but not supported by TTN at this time).
LMIC_setLinkCheckMode(0);
break;
case EV_RFU1:
DEBUG(F("EV_RFU1"));
break;
case EV_JOIN_FAILED:
DEBUG(F("EV_JOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_REJOIN_FAILED:
DEBUG(F("EV_REJOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_TXCOMPLETE:
DEBUG(F("EV_TXCOMPLETE (includes waiting for RX windows)"));
if (LMIC.txrxFlags & TXRX_ACK)
DEBUG(F("Received ack"));
if (LMIC.dataLen) {
DEBUG(F("Received "));
DEBUG(LMIC.dataLen);
DEBUG(F(" bytes of payload"));
}
// Schedule next transmission
os_setTimedCallback(&sendjob, os_getTime()+sec2osticks(TX_INTERVAL), do_send);
break;
case EV_LOST_TSYNC:
DEBUG(F("EV_LOST_TSYNC"));
break;
case EV_RESET:
DEBUG(F("EV_RESET"));
break;
case EV_RXCOMPLETE:
// data received in ping slot
DEBUG(F("EV_RXCOMPLETE"));
break;
case EV_LINK_DEAD:
DEBUG(F("EV_LINK_DEAD"));
break;
case EV_LINK_ALIVE:
DEBUG(F("EV_LINK_ALIVE"));
break;
default:
DEBUG(F("Unknown event"));
break;
}
}
void do_send(osjob_t* j){
// Check if there is not a current TX/RX job running
if (LMIC.opmode & OP_TXRXPEND) {
DEBUG(F("OP_TXRXPEND, not sending"));
} else {
LoraMessage message;
//-----Temperature-----//
//-----Humidity-----//
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("Temperature: "));
temperature = HDC.readTemperature();
DEBUG(temperature);
message.addUint16((temperature + 18) * 771);
delay(2000);
DEBUG(F("Humidity: "));
humidity = HDC.readHumidity();
DEBUG(humidity);
message.addHumidity(humidity);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----Pressure-----//
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
float altitude;
pressure = BMP.readPressure()/100;
altitude = BMP.readAltitude(1013.25); //1013.25 = sea level pressure
DEBUG(F("Pressure: "));
DEBUG(pressure);
message.addUint16((pressure - 300) * 81.9187);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----Lux-----//
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("Illuminance: "));
lux = TSL.readLux();
DEBUG(lux);
message.addUint8(lux % 255);
message.addUint16(lux / 255);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----UV intensity-----//
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
DEBUG(F("UV: "));
uv = VEML.getUV();
DEBUG(uv);
message.addUint8(uv % 255);
message.addUint16(uv / 255);
delay(2000);
#endif
//-----PM-----//
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
uint8_t attempt = 0;
while (attempt < 5) {
bool error = SDS.read(&pm25, &pm10);
if (!error) {
DEBUG(F("PM10: "));
DEBUG(pm10);
message.addUint16(pm10 * 10);
DEBUG(F("PM2.5: "));
DEBUG(pm25);
message.addUint16(pm25 * 10);
break;
}
attempt++;
}
#endif
// Prepare upstream data transmission at the next possible time.
LMIC_setTxData2(1, message.getBytes(), message.getLength(), 0);
DEBUG(F("Packet queued"));
}
// Next TX is scheduled after TX_COMPLETE event.
}
void setup() {
#ifdef ENABLE_DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600);
#endif
delay(3000);
// RFM9X (LoRa-Bee) in XBEE1 Socket
senseBoxIO.powerXB1(false); // power off to reset RFM9X
delay(250);
senseBoxIO.powerXB1(true); // power on
// Sensor initialization
DEBUG(F("Initializing sensors..."));
#ifdef VEML6070_CONNECTED
VEML.begin();
delay(500);
#endif
#ifdef HDC1080_CONNECTED
HDC.begin();
#endif
#ifdef BMP280_CONNECTED
BMP.begin(0x76);
#endif
#ifdef TSL45315_CONNECTED
TSL.begin();
#endif
#ifdef SDS011_CONNECTED
SDS_UART_PORT.begin(9600);
#endif
DEBUG(F("Sensor initializing done!"));
DEBUG(F("Starting loop in 3 seconds."));
delay(3000);
// LMIC init
os_init();
// Reset the MAC state. Session and pending data transfers will be discarded.
LMIC_reset();
// Start job (sending automatically starts OTAA too)
do_send(&sendjob);
}
void loop() {
os_runloop_once();
}